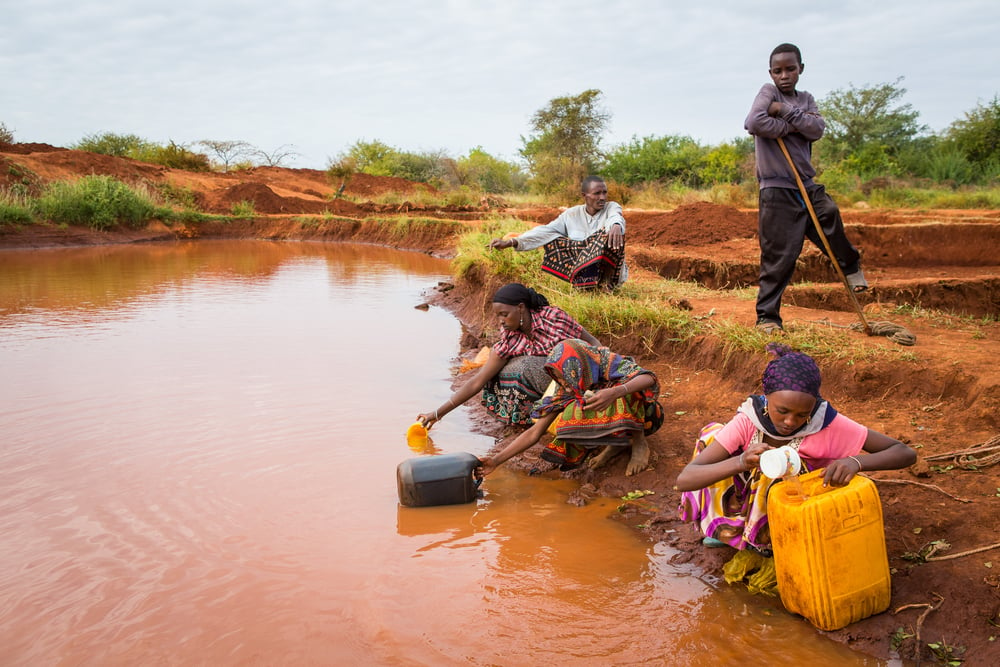
 |
| Gayo village in Ethiopia, where women are collecting contaminated pond water for drinking and other household purposes. |
Soybeans As Flocculants
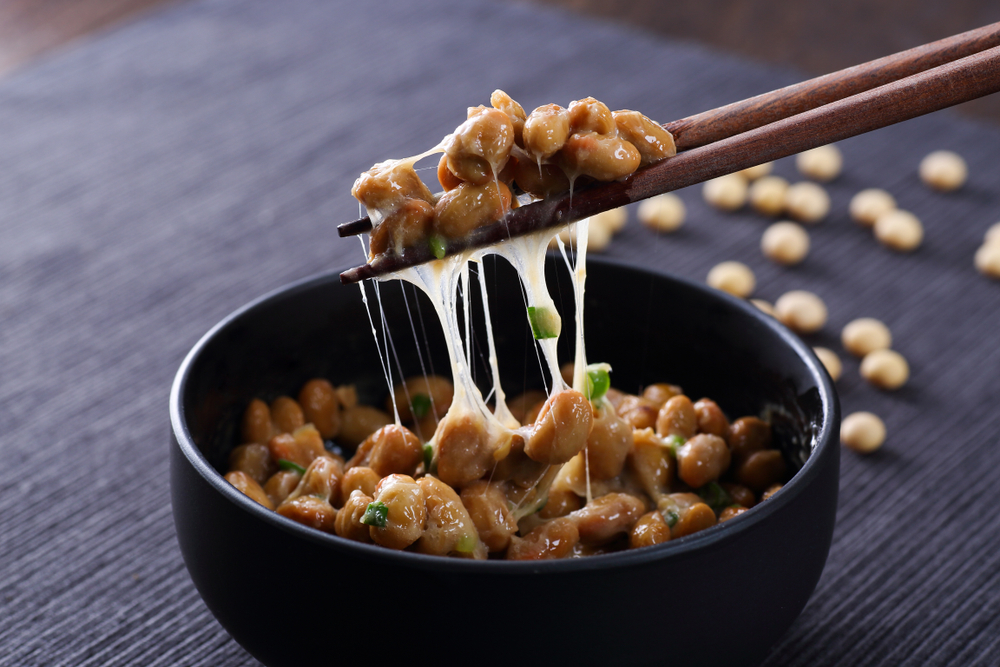 |
Natto is a popular dish in Japan, prepared
by bacterial fermentation of soybeans.
Gamma-Polyglutamic acid is a major constituent of Natto.
Using this biomolecule, the dirt-coagulating
chemical PGα21Ca is manufactured.
|
How Are
Soybeans Quenching The Thirst Of Millions?
Dev Lunawat
Soybeans pack a serious punch of proteins, fiber and omega-3, but
did you know they could also serve a higher purpose as inexpensive and
effective water purifiers?
Yes, that’s right. Soybeans are being used to treat
contaminated water sources for displaced refugees from Somalia.
Access to safe, potable water is a comfort that is not enjoyed by
everyone on the planet, and as we have increasingly seen in recent years, the
water crisis is real.
Water, water everywhere and not
a drop to drink…
Water is the elixir of life, the fuel for sustaining existence, a
salient element of socio-economic development, food production and healthy
ecosystems around the globe.
The next time you gulp down a glass of water or pop open a can of
soda (which contains water), ask yourself an important question… where does
that water come from?
If you’re drinking an Indian Cola, then it most certainly includes
treated rainwater.
A beverage from the Maldives might have seawater instead.
As you likely know, the world is in the early stages of a “Global
Water Crisis” that only threatens to get worse.
In essence, only 0.007% of Earth’s water is safe to drink for the
6.8 billion people on the planet. Clearly, this stat sets the odds against us.
Hence, it is critical that we find sustainable methods to source
clean water from saline/undrinkable areas. However, how do soybeans help
to solve this problem?
Polyglutamic acid
Soybeans, when fermented, produce a sticky paste known as Natto, which
is often enjoyed as a popular ingredient in Japanese food.
The bacterial fermentation that goes into producing this sticky
substance produces polyglutamic acid.
This class of amino acids can be used to develop a high polymer
flocculant, PGα21Ca.
This is a complex bio-molecule composed of calcium sulfate,
calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, aluminum sulfate and (most importantly)
polyglutamic acid.
PGα21Ca is a safe and eco-friendly binding agent (generally in the
form of a white powder) that coagulates with the solid particles present in a
liquid, such as water.
When added to contaminated water, it readily binds with all the
grime and dirt present in the liquid, and owing to the increased weight of
those solid particles, it settles at the bottom of a given container.
Is it safe to drink?
Not quite yet… before the water is fully treated and ready to
drink, it’s important to understand the physics behind the process of
flocculation.
Flocculation is a procedure whereby the impurities present in a
dirty solution can be filtered out in the form of flakes, either impulsively or
through the addition of a clarifying agent (PGα21Ca, in our case).
But how is that different from our conventional precipitation
methods?
The action of flocculants differs slightly here. In precipitation
methods, you would usually add a precipitant to the solution and obtain a
solid, insoluble mass of extremely fine particles.
Then, after tedious electrolytic procedures, you would obtain
completely separated impurities floating in the mixture.
This procedure is expensive and extensive, so it’s usually carried
out in laboratories and industries to separate heavy metals from water.
Drought-hit areas in poorly developed regions have no access to
such “clean benefactions”, so this soybean formulation has been a boon for
global society.
Although this soybean extract can remove the major visible
pollutants found in water, it cannot “completely” purify wastewater from
dangerous bacteria.
Therefore, it is imperative to apply more resources that are
accessible and affordable as a means of fully purifying water.
The age-old boiling technique will do the job in this case, as it
can remove the remaining populations of bacteria that could cause you
harm.
Take a look at this amazing innovation in action!
Fun Facts about Soybeans
Now you can see how a simple commodity like soybeans can be turned
into a lifesaving breakthrough using nothing but a pinch of science, an
analytical mind, and a worthy purpose.
However, before you go out there to change the world in your own
way, take a look at some other surprising facts about soybeans that you
probably didn’t know:
1. The oil extracted from soybeans
can be used as an environmentally friendly fuel for diesel engines with lower
carbon monoxide emissions.
2. Soy ink is used in textbooks
and newspaper printing.
3. Soybean wax or soy wax finds
its way into cleaning agents, haircare products and candles.
4. An acre of soybeans can produce
82,368 “eco-friendly” crayons.
5. Soybeans are used in the
adhesive, plastics and textile industries.
6. During the Civil War, when real
coffee was scarce, soybeans were a substitute brew that didn’t taste half bad!
Dev is an
undergraduate (Bachelor of Science) from St. Xavier’s College (India). He
watches a lot of anime and documentaries on the universe and wildlife. He
spends most of his time engaging in sports and exercise. He has represented his
state at the National Volleyball tournament, in India. Along with that, he has
a flair for sketching, photography and would be glad to take up gardening as a
career.
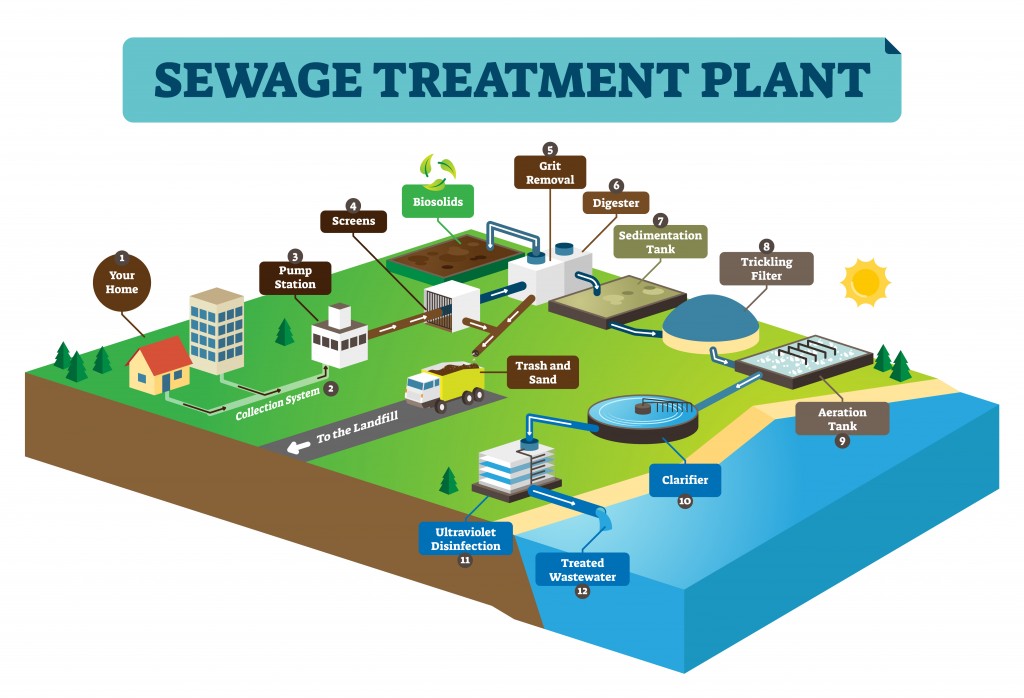 |
| Sewage treatment plants are a common necessity in almost every city of the world. However, for regions where clean drinkable water is scarce and people have no access to clean water due to economic reasons, soybean water purification has proved a boon for life |

No comments:
Post a Comment