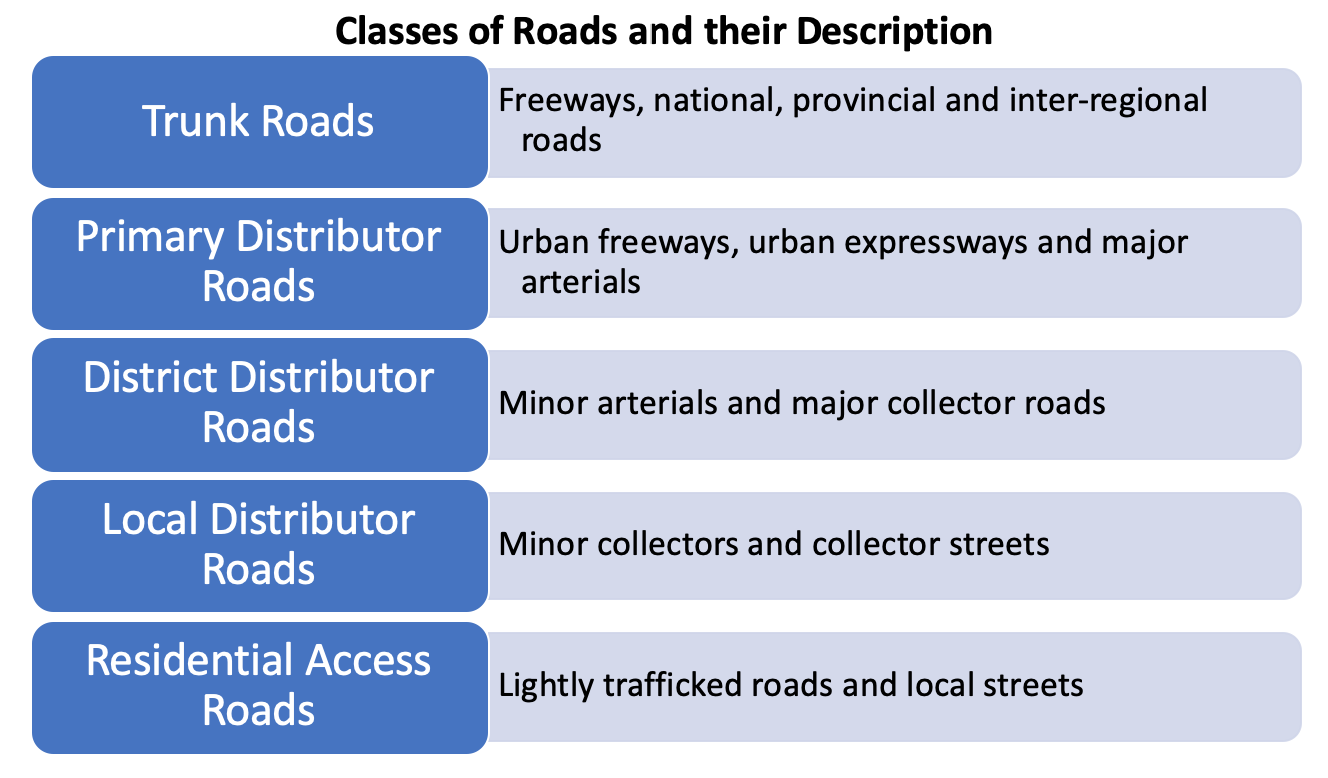
..............................................................................................................................................................
Unusual Uses for WD-40
 For certain
applications there's room for a product like WD-40, but most other times it's
better to use a dedicated solvent first followed by a dedicated lubricant after
For certain
applications there's room for a product like WD-40, but most other times it's
better to use a dedicated solvent first followed by a dedicated lubricant after
By mikeasaurus
Instructables
WD-40
is a low viscosity solvent with an added lubricant, and probably the item found
in almost every tool box and workshop around the world.
The
story goes that development of a corrosion prevention solution took 40 tries to
create a water displacing formula, the name water displacement 40 stuck.
The
ubiquitous and most recognized brand of solvent/lubricant brings with it a lot
of myths, and ire, regarding its efficacy.
This
product is used in all kinds of ways, but there's something very important to
consider before reaching for the blue can.
.
WD-40 is primarily a petroleum-based volatile solvent that evaporates leaving behind a non-volatile lubricant
.
WD-40 is primarily a petroleum-based volatile solvent that evaporates leaving behind a non-volatile lubricant
Meaning
that the solvent penetrates and does its job removing grime and then evaporates
and leaves behind a thin film of oil.
It's
important to know just what WD-40 is, and what it isn't.
For
certain applications there's room for a product like WD-40, but most other
times it's better to use a dedicated solvent first followed by a dedicated
lubricant after.
Just
like a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner isn't the best at being a shampoo or
conditioner, neither is WD-40.
An
important distinction with WD-40:
The
MSDS for WD-40 shows that it's mostly a penetrating solvent with some oil once
the solvent is gone.
There
are other varieties of WD-40 on the market that do different things,
specifically a version that is a lubricant that has no solvent (see can on the
right in the picture below).
If
you're looking for just a lubricant then standard WD-40 is not the right tool
for the job, which is where some confusion and myths arise about this product.
In
this Instructable we'll focus on the ubiquitous blue can of WD-40 (solvent with
some oil aftermath) and explore actual unusual uses.
Whatever
your feelings on this sometimes slippery substance, you're sure to find some
unusual uses for WD-40 below.
Step
1: De-grease Your Hands
Applying
a spray of solvent to your greasy hands can help cut into the grime and clean
your hands before applying a soap lather.
 .
.
Spray your hands over a trash bin or other contained area and then rub your hands together, working the solvent into your greasy hands with your fingers to remove any grease buildup.
 .
.Spray your hands over a trash bin or other contained area and then rub your hands together, working the solvent into your greasy hands with your fingers to remove any grease buildup.
 After
your hands have been degreased, head over to your wash basin and wash your
hands with plenty of soap to remove the remaining lubricant the WD-40 left.
After
your hands have been degreased, head over to your wash basin and wash your
hands with plenty of soap to remove the remaining lubricant the WD-40 left.
Step
2: Remove Stickers / Decals
 No
matter how careful I am I always manage to rip the sticker, making removal so
much more difficult. WD-40 to the rescue!
No
matter how careful I am I always manage to rip the sticker, making removal so
much more difficult. WD-40 to the rescue!
Blast
your sticker with this slippery lubricant and let sit for about 5 minutes.
 I
find that saturating a paper towel and leaving that on top of the sticker works
great at keeping the lubricant on the sticker and contained.
I
find that saturating a paper towel and leaving that on top of the sticker works
great at keeping the lubricant on the sticker and contained.After a few minutes you should see a notable change in the sticker as it's absorbed the WD-40, and should peel right off.
Step
3: Crayon + Marker Removal
When
regular cleaner just won't do, WD-40 steps in to make cleanup easier.
Spray
crayon marked area and let sit for a few minutes (saturating a square of paper
towel to stick to vertical surfaces can help), then rub area with a lint free
cloth to remove the crayon. (Thanks for the pictures, Troy)
After
the crayon has been removed, clean the wall with regular household cleaner to
and a cloth remove the WD-40 residue.
As
with all stain removal solutions, test in an inconspicuous area first to ensure
you won't damage your walls.
Step
4: Remove Permanent Marker From Walls, and Other Non-porous Surfaces
(Sometimes)
The
solvent in WD-40 is strong enough to penetrate and remove permanent marker, but
the surface that the marker is on make a huge difference.
 If
the marked surface has a glossy paint coating, like the walls in kitchens and
washrooms, you're likely to get the marker off. Ditto with tile.
If
the marked surface has a glossy paint coating, like the walls in kitchens and
washrooms, you're likely to get the marker off. Ditto with tile.However, if your wall has a matte finish you probably won't get all the marker off using WD-40.
Soak
a paper towel or rag with WD-40 and apply it directly onto the permanent marker
on the wall.
Allow
the solvent to make contact with the wall for about 30 seconds, then gently rub
the area in small circular motions.
 If
you apply too much pressure right away you risk smearing the marker around the
wall, so go slow and apply more pressure to the rubbing motion once most of the
marker has been removed.
If
you apply too much pressure right away you risk smearing the marker around the
wall, so go slow and apply more pressure to the rubbing motion once most of the
marker has been removed.
If
you have a matte or porous finish then the image above is likely as good as the
cleanup is going to get.
If
you're determined to remove the marker using this method then apply more WD-40
and keep scrubbing.
Repeat
the process of soaking a rag in WD-40 and applying it directly to the affected
area, letting it sit for a few seconds before buffing and removing the marker.
I
was able to remove the marker here on a semi-gloss wall with under 5-minutes of
work.
Step
5: Keep Shovel Snow Free
Since
WD-40 has lubricating properties, use it to keep things you want clean nice and
slippery.
 Spraying
some WD-40 on your snow shovel face can clean the shovel face and prevent snow
from sticking to whatever was scooped up previously, and the light oil finish
after the solvent has evaporated keeps the shovel nice and slippery. (nice
boots there, Jessy!)
Spraying
some WD-40 on your snow shovel face can clean the shovel face and prevent snow
from sticking to whatever was scooped up previously, and the light oil finish
after the solvent has evaporated keeps the shovel nice and slippery. (nice
boots there, Jessy!)
Spray
a light coating over the shovel face and wipe off to remove any substances that
might be on the shovel.
Then
apply a second light coat and let stand for about a minute to let the solvent
evaporate. Then, you're ready to go!
Depending
on how much shoveling you're doing you may need to reapply, so keep the spray
can handy.
Step
6: Remove Stuck Ring
Since
many banged knuckles come from a workshop, WD-40 is a handy remedy that can
quickly slip a tight ring off a fat finger.
 Spray
your ring with a liberal dose of WD-40 and then work the ring around your
finger, allowing the low viscosity oil to run in between your ring and skin.
Spray
your ring with a liberal dose of WD-40 and then work the ring around your
finger, allowing the low viscosity oil to run in between your ring and skin.
The
oil will lube up your finger and (hopefully) let your finger slip out from the
constricting ring.
Step
7: Clean Stainless Steel Sinks
Though
stainless steel is a robust material for the kitchen, it can get watermarks and
fingerprint stains.
Not
only will it remove stains, the remaining oil from WD-40 also helps protect the
surface from getting new marks in the future.
Since
WD-40 is a petroleum-based product, make sure you clean anything it is used on
in the kitchen thoroughly afterwards.
Step
8: De Rust Cast Iron Tools
Probably
the most practical application for WD-40 outside of being a lubricant is it's
use to clean cast iron.
Use
a 100-120 grit sandpaper to gently scrub in small circles over the entire
affected area.
Use
a rag to wipe off the loose rust and debris, then apply more WD-40 and repeat
until all large portions of rust are removed.
 For
stubborn areas saturate again with WD-40 and use some 00 steel wool, rubbing in
small circles over the entire area.
For
stubborn areas saturate again with WD-40 and use some 00 steel wool, rubbing in
small circles over the entire area.
The
steel wool is great for getting into the small crevices of the cast iron, and
providing a protective oil sheen to the cast iron. (That's a good looking
spindle sander, Troy).
Step
9: Lubricate Vinyl Records
This
is probably the most contentious application for WD-40 on the Internet. Period.
But, before you vinyl music purists put my head on a spike, hear me out!
There
is some merit to using WD-40 on vinyl records.
 Since
WD-40 has solvents it's great for dissolving waxy grime from your records, and
evaporates quickly leaving a thin oil behind to lubricate the record stylus.
Since
WD-40 has solvents it's great for dissolving waxy grime from your records, and
evaporates quickly leaving a thin oil behind to lubricate the record stylus.
However,
it's those same solvents that give people pause when using WD-40 on a plastic
like vinyl.
The
reason to even consider using WD-40 in an application like this is the one-two
punch of solvent (to remove grease) and lubricant (smooth vinyl).
I
can only speak from my own personal experience, and I have yet to see any
deleterious results.
However,
if you're unsure you can always use two separate applications of a vinyl-safe
cleaning solvent and then a lubricant.
Step
10: Bonus: Where NOT to Use WD-40
As
a bonus, it's important to know where not to use WD-40.
 In
the intro I mentioned that WD-40 is a solvent first, with a light oil remaining
after the solvent evaporates.
In
the intro I mentioned that WD-40 is a solvent first, with a light oil remaining
after the solvent evaporates.
You'd
be surprised how people use WD-40 primarily as a lubricant, which is only going
to make things worse.
Though
there's loads of good applications for WD-40, there's plenty of places that you
shouldn't use it. Here's a few:
Electronics:
This might seem obvious, but you'd be surprised at where electronics are
hiding.
An
often overlooked area could be the buttons on your smartphone or music player,
all the way to something less obvious like the lens for your digital camera.
The
solvents in WD-40 can break down some plastics, and the low viscosity of WD-40
makes sure the solution penetrates deep.
Solution:
If possible open the device and clean by hand using very little silicone spray.
Bike
chains, door hinges: The lubrication will work as intended for all these
applications, but the residue left over can also attract dirt and dust thereby
negating the oil benefits after the initial application.
 Solution:
Clean bike chain with an old toothbrush to remove debris. Use bike chain oil
and wipe clean with a rag.
Solution:
Clean bike chain with an old toothbrush to remove debris. Use bike chain oil
and wipe clean with a rag.
Door
locks: If your door lock is stuck, the solvent in WD-40 might help is get
loose, but there's not enough lubricant left over to help the tumblers move
freely over the long term.
Solution:
Use a graphite powder, designed to stay slippery and made especially for locks.
Rubik's
Cube: WD-40 is not a lubricant, it's a solvent. Using WD-40 on some plastics
can cause them to break down or melt.
Solution:
Use a silicone spray.
Do
you have your own unusual use for WD-40?I want to see it!
Happy
making :)
Our Story
The seeds of Instructables
germinated at the MIT Media Lab as the future founders of Squid Labs built
places to share their projects, connect with others, and make an impact on the
world. One of these early places was a blog Zeroprestige, which was an open
source hardware experiment for kitesurfing. Here they documented their
hand-sewn kites, plywood boards, and other general mayhem that happens when
PhDs and high winds collide.
As a result of freely sharing
our work, we met a ton of great people, received great opportunities, and were
smacked in the face with the need for a web-based documentation system.
Instructables became that
documentation system in 2005, as an in-house project of Squid Labs. When they
weren't solving interesting problems like solar panels for driveways,
efficiently harnessing human power, or strain sensing ropes, you could find
them sharing Instructables from the workshop. From cooking to 3d printing, to
making just about anything fly, Instructables became the recipient of countless
hours of tinkering, soldering, stitching, frying, and fun, making just about
anything.
Instructables was officially
spun out of Squid Labs in the summer of 2006, and has gone on to grow from a
modest hundreds of projects to over one hundred thousand. The community that
now calls the site home, is an amazing mix of wonder from around the world.
Every day we continue to be amazed by the imagination, curiosity, and simple
awesomeness of everyone who shares their creations with us on Instructables.
https://www.instructables.com/id/Unusual-Uses-for-WD-40/

You might also like:
CLICK HERE . . . to view . . .
..................................................................................................................................................................
The Interesting History of WD-40
CLICK HERE . . . to view . . .









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/200433926-001-F-57a5bd115f9b58974aee8234.jpg)