........................................................
Tubes vs. Pipes
 What are the main differences?
What are the main differences?
Francesco
Grillo
Understand the 12 significant differences between steel tube and
steel pipe in detail from the industry experts. Resolve the tube vs. pipe
confusion.
Ever wondered what to call a cylindrical
section? A pipe or is it a tube?
Confusing, isn’t it?
Both the tools appear to be working on the same hollow cylindrical
concept. Regardless of how similar they appear, tube and pipe have dramatically
different characteristics.
What exactly is the actual difference between pipe and tube?
Let’s hunt pipe vs tube down!
The difference is in the details!
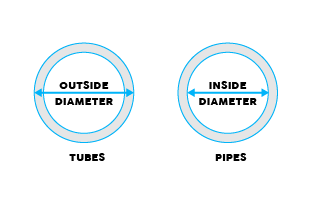
1. DIAMETER
While determining the actual size, tubes and pipes are
measured differently.
A tube is measured with the help of exact
outside diameter (OD) with a set range of wall thickness. The
wall thickness is vital as the tube’s strength is dependent on it.
On the other hand, we measure a pipe by using a nominal
outside diameter. The most important property is the capacity or the inside
dimension (ID).
Pipes accommodate larger applications with sizes that
range from a half-inch to several feet. Tubes are generally used in
applications that require smaller diameters. While
a 10-inch pipe is common, it is rare that you will find a 10-inch tube.
2. WALL THICKNESS
The wall thickness is an important factor while
differentiating between pipes and tubes.
The thickness of a tubing is often specified by a gauge
for thinner thickness and for thicker tubing it is
indicated by fractions of an inch or millimeter. The normal
range of tubing is 20 gauge, which is 0.035 inch up to a thickness of 2 inches.
The wall thickness of a pipe is referred to as a
pipe schedule thickness. The most common pipe schedules
are:
• SCH20,
• SCH40,
• and
SCH80.
SCH40 is the most common and SCH80 is quite heavy.
3. STRUCTURE
A tube’s structure does not have to be round always. It can be square or rectangular too. They are
usually seam welded.
Pipe, on the
other hand, is always round and rigid. It cannot be
shaped easily without the use of a special equipment. Pipes are usually
seamless and pressure rated to avoid leakages as they usually carry liquids or
gases.
4. TOLERANCE
Comparing the tolerance of both tubes and pipes, the
tolerance for pipes is looser than tubes. Pipes are usually used for
transporting or distributing, therefore the properties of pressure,
straightness, or roundness are strictly specified.
5. MANUFACTURING PROCESS
The materials and the manufacturing techniques of both
pipes and tubes differ.
Tubes require a higher level of processes, tests, inspection. As a result,
the delivery period is longer too. The yield of tubes is comparatively much
lower than the pipes.
Instead, the manufacturing process of a pipe is easier in
comparison to tubes and more often undergoes mass production.
6. COST
The manufacturing of tubes utilizes much more labor,
energy, and material. Therefore, in case of same material, the production
cost of tubes is usually higher than pipes.
The manufacturing process of pipes is easier and they are
always manufactured in large lots. This lead to a cutting in the cost of
pipes.
7. USES
Pipes are used mainly for transportation of fluids and
gases like water, oil, gas, propane
etc. Therefore, the outside and inside diameter is the key measurement and
pressure rating is important.
At the opposite, the main use for tubes
is for structural purposes such as scaffolding. They are
often put to use in applications that call for precise outside diameters.
Therefore, the outside diameter is vital as it indicates how much the tube can
hold.
8. MATERIAL
Pipes are usually made of carbon steel or low alloy steel.
Tubes instead are made of mild steel, aluminum, brass,
copper, chrome, stainless steel, etc.
The difference in materials is also a reason for the
difference in the cost and applications.
Some widely used steel pipe standards or piping classes
are:
• The
API range – now ISO 3183. E.g.: API 5L Grade B – now ISO L245 where the number
indicates yield strength in MPa
• ASME
SA106 Grade B (Seamless carbon steel pipe for high temperature service)
• ASTM
A312 (Seamless and welded austenitic stainless steel pipe)
• ASTM
A36 (Carbon steel pipe for structural or low pressure use)
• ASTM
A795 (Steel pipe specifically for fire sprinkler systems)
9. MECHANICAL AND CHEMICAL
PROPERTIES
The pressure rating, yield strength, ductility properties
are more important for pipes. However, for tubes, the hardness, tensile
strength, and high precision is the key to high quality.
Carbon, Manganese, Sulphur, Phosphorus, and Silicon are
the main chemical elements for pipes. While for tubing, the microelements are
very important to the quality and process.
10. SURFACE FINISHING
Pipes need to be painted or coated to anti corrosion or
oxidation for outdoor field transporting or underground transporting.
Tubes often go through sour cleaning or special polish
treatment for their particular field uses.
11. CONNECTION
Connecting one pipe to another is much more of a labor intensive
process as it requires welding,
threading, or flanges along with its relevant equipment.
On the contrary, tubes can be joined quickly and
effortlessly with flaring, brazing, or coupling. Tube assemblies can also take
place through tube fittings where high standards of construction are
needed.
Pipe welding is safer that tube joining.
12. THE ENDS
Pipe ends are usually in a plain or beveled form. Whereas, tubes generally come with coupling ends
or special end finishes like irregular ends, special screw thread etc.
Any further doubts on this topic? If
you want to have more information or you want to share your opinion, contact us
at info@steelavailable.com.
We are Steel
Available, an online supplier relationship management
and sourcing platform. We aim to connect suppliers and buyers from the heavy
industry. We are developing the first ecosystem in the heavy industry which
will allow clients to efficiently manage and automate their supply chains using
web-based tools and services. Our goal is to reduce the hidden risk in value
chains. We do it by providing the information that matters, from compliance to
quality assurance, creating value for all stakeholders.
To get more information, please download our brochure.
Written by:
Francesco Grillo
Co-founder & CEO @SteelAvailable





No comments:
Post a Comment