
..............................................................................................................................................................
Biogas
A Beginners Guide – Home to
Commercial Digester Systems
anaerobic-digestion.com
What
is Biogas?
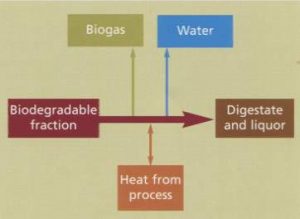
Biogas
is generated during anaerobic digestion (AD) when microorganisms break down (by
eating it) organic materials in the absence of air (or oxygen).
Biogas
is mostly methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with very small amounts of
water vapor and other gases. The carbon dioxide and other gases can be removed,
leaving only the methane.
Methane
is the primary component of natural gas. The material that flows out after
anaerobic digestion happens is called “digestate.”
Digestate
is a wet mixture that is usually separated into a solid and a liquid. Digestate
is rich in nutrients and can be used as fertilizer for crops.
In
the process of anaerobic digestion, as mentioned above, the bacterial breakdown
of organic materials in the absence of oxygen produces biogas.
The
process occurs in the following four steps:
· Hydrolysis: large polymers are broken down by enzymes
· Acidogenesis: acidogenetic fermentations are most
important, acetate is the main end product. Volatile fatty acids are also
produced at this stage along with carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
· Acetogenesis: breakdown of volatile acids to acetate
and hydrogen.
· Methanogenesis: acetate, hydrogen are converted to
methane and carbon dioxide.
And,
the result is the sustainable renewable energy source (sometimes also spelled
as) “bio-gas”.
Why
is Biogas Important?
Biogas
is important because it is a rare and badly needed commodity in these times of
climate change. it’s important as a source of green and clean energy. It’s also
important in other ways as well.
a) It Can be a Significant Contributor to Reducing
Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions
In
December 2019 the World Biogas Association presented the UNFCCC with an
industry commitment.
Major
biogas industry players committed to delivering a 12% reduction in global
greenhouse gases emissions by 2030 provided world governments help unlock the
sector’s potential.
b) An Untapped Material Supply with Scope to Enlarge
As
we said at the start, it is made from biological breakdown of organic matter.
There is a huge quantity of waste organic material available that can be used.
The
waste organic material which can be used includes feed materials (feedstocks)
such as :
· all kinds of animal dung/ manure,
· kitchen waste, and waste from commercial food processing
· dead plants etc. including the parts of food crops
which are not food, such as the stems and leaves.
The
important point about this is that it can be used as gaseous fuel. Methane is a
gas which provides good caloric values when used as fuel.
What
is more, at the moment less than one tenth of the available waste organic
matter which could be easily be digested to make biogas is being used.
c) It’s Already a Cooking Fuel in India and Similar
Nations
Biogas
produced from the anaerobic disintegration of manure in small-pits in India is
called Gobar Gas. Many other developing nations, including China, also make
their biogas this way
The
gobar gas is also very important because it is estimated that over two million
households in India already make their own gobar gas for cooking.
They
do do this easily using dung from their own cattle. It is popular source of
fuel in many parts.
d) It Recycles as Part of a Circular Economy
Anaerobic
digestion delivers two types of recovery from organic waste in a virtuous
carbon circle:
Agronomic waste recovery: with the production of compost, and energy in the
form of biogas, electricity or heat. This technology is widely used across
Europe and is gaining momentum all around the world.
It provides an
answer to one of the current challenges facing the farming sector.
The sector
must now design new models of production taking into account environmental
constraints, big reductions in carbon emissions, while still improving competitiveness
and feeding the ever-rising population.
Industrial and Commercial waste recovery: again, with the production of compost and energy but
more wide-ranging types of organic waste, from the likes of the food and
beverage industries.
Plus, waste
from municipalities, such as green waste from parks and gardens and the
byproducts from wastewater treatment plants.
Unlike
incineration, precious organic material is retained to provide fertilizers and
soil improver which is a very important function.
If the output
from a biogas plant is made into charcoal (char) it can be put back on the land
to improve soil quality while also acting as carbon storage (also known as
carbon sequestration).
What
is the Cost of the Source of Biogas Energy
Often
there are no charges for this energy source. A large proportion of the raw
materials, in particular manure and plant residues, are generally available
free of charge.
There
is no transport needed when the digester is built on-farm.
Using
“waste” raw materials has the greatest economic potential for the production of
biogas.
These
materials may even be more cheaply treated using AD plants, where taxes are
charged for disposing that material to landfill.
Compare
that with the cost of mining fossil fuels for energy!
What
is Biogas Used for?
It
is a great gas to use for domestic cooking and that’ what gobs gas is used for
as described earlier.
In
agriculture it can be used on-farm for heating farm buildings and the
farmhouse. Any excess can be used for generating electricity which can be sold
for an income.
Biogas
can be used for electricity production at sewage works, in a CHP gas engine,
where the waste heat from the engine is conveniently used for heating the
digester.
If
purified (upgraded) it can be compressed to replace compressed natural gas for
use in vehicles, where it can fuel an internal combustion engine.
Or
it can be used in fuel cells. in both the later uses it is a much more
effective displacer of non-renewable carbon dioxide than the normal use in
on-site CHP plants.
What
is Biogas Made of
The
composition of biogas varies depending upon the substrate composition, as well
as the conditions within the anaerobic reactor (temperature, pH, and substrate
concentration).
Landfill
gas is a form of this gas. It typically has methane concentrations around 50%.
Digester
gas produced using advanced waste treatment technologies can produce biogas
with 55%–75% methane, which for reactors with free liquids can be increased to
80%–90% methane using in-situ gas purification techniques.
What
is a Biogas Generator?
A
biogas generator is any machine, mechanical plant and equipment that converts
waste into clean energy!
Many
people make their own Biogas Generator to produce their own “natural” gas.
For
example, you can do it in a way that transforms grass clippings, food waste and
livestock manure into renewable biogas energy with a homemade biogas generator
What
is Biogas Production?
It’s
the making of this bio-fuel.
Most
biogas production takes place in processing facilities (plants) which rely on
anaerobic digestion, a fermentation process in which waste is digested by
microbes to produce a predominantly methane gas (biogas).
Almost
any organic waste can be used in the process, though factors such as ph and
temperature affect the gas production.
The
Working of Biogas Plants
During
the process, the micro-organisms transform biomass waste into biogas (mainly
methane and carbon dioxide) and digestate.
Higher
quantities of biogas can be produced when the wastewater is co-digested with
other residuals from the dairy industry, sugar industry, or brewery industry.
For
example, while mixing 90% of wastewater from beer factory with 10% cow whey,
the production of biogas was increased by 2.5 times compared to the biogas
produced by wastewater from the brewery only.
The
Types of Biogas Plants
Common
biogas plant types can be differentiated according to methods of substrate
feed, biogas collecting methods, materials used for their construction,
horizontal or vertical digester position, underground and above-ground digester
location and according to additional equipment used.
There
are many different types. Here are some examples:
Batch
biogas plants
Wet
Process Batch Digester (for example a laboratory trial digester use to find
likely gas output/ optimum substrate retention time)
Dry
Digester (Tunnel)
Vertical
DRANCO (DRy ANaerobic COmposting) process
Continuous
load plants
· Single Stage Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
· Two Stage CSTR
· Plug Flow Reactor
· Upward Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor
· Anaerobic Lagoon
The
Biogas Digester
A
“digester” is simply a biogas plant by another name. sometimes the digester may
be referred to as just the big tank reactor where fermentation takes place.
The
Importance of Bio-gas
The
importance of biogas lies in its ability in converting organic waste into
energy.
Not
only that it utilizes nature’s elegant tendency to recycle substances into
productive resources.
It’s
generation recovers waste materials that would otherwise:
· pollute landfills;
· be left around to make methane to further raise the
global temperatures
It’s
also important as it can treat waste on-site enabling the output nutrients to
be put back into the land.
Moreover,
its usage does not require fossil fuel extraction to produce energy.
Biogas
Advantages
Biogas:
1. Is Eco-Friendly
2. It’s Generation Reduces Soil and Water Pollution
3. It’s Generation Produces Natural Organic Fertilizer
4. It’s a Simple and Low-Cost Technology That
Encourages A Circular Economy
5. It’s a Healthy Cooking Alternative For Developing
Countries.
Disadvantages
of Biogas
· New Technological Advancements needed to make these
plants easier to operate and lower costs
· Contains Impurities
· Effect of Temperature on it’s Production means they
work best in hotter climates unless heavily insulated and heated against the
cold
· Less Suitable For Dense Metropolitan Areas.
Biogas
Yield
The
variables that can make a difference to the yield of bio-gas include:
· the feedstock you use (crop, waste, manure etc. )
· the length of time left in the digester
· the mix of different organic materials
· the efficiency of reactor mixing
· the pH of the reactor
· the build-up of inert materials such as grit, sand and
other unwanted materials such as inadvertent plastics which enter the reactor
tanks.
· the presence or absence of importance of trace
nutrients.
If
your feedstock has been left in storage for a long amount of time it may have
already started breaking down. Tables are available which show the potential
bio-gas yields of common feedstocks.
The
Methane Content
The
gas has a composition which is usually 50% to 80% methane and 20% to 50% carbon
dioxide with traces of gases such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen.
In
contrast, natural gas is usually more than 70% methane with most of the rest
being other hydrocarbons (such as propane and butane) and traces of carbon
dioxide and other contaminants.
Biogas
Boiler Design
Biogas
can then be used to generate electricity, as a boiler fuel for space or water
heating.
Depending
on the design of the boiler the raw gas may, or may not, first be upgraded to
natural gas pipeline quality.
If
upgraded the biomethane produced can be used to fuel any standard boiler
designed for pipeline distributed “natural gas”.
Steam
boilers are available which can be operated with different liquid and gaseous
fuels, such as natural gas, fuel oil, biogas, and with multi-fuel firing units.
Biogas
Heating System
A
biogas heating system is created when the hot water from a gas-engine
(generator) jacket, and generator or exhaust gas heat exchanger, is distributed
through a network of pipes and is used for home, farmhouse, drying room, barn,
factory, warehouse, or work-space heating.
Sometimes
the heating system will be provided heat from a bio-gas fueled boiler
AD
Plant Cost
Although
a number of cost calculators are offered on websites, very little data on
biogas cost is published.
The
truth is that these facilities vary so much that to put a price tag on them
isn’t possible without deciding first on a design, and from that estimating
tank sizes etc. Only once site specifics are known is it reasonable to price
these AD Plants.
Capital
costs for a larger ad facility (50,000 tons per year) are expected to be over
$20 million.
Small
home digesters may be bought for about $500.
What
is its Future?
The
possibilities of increased use of anaerobic digestion as an effluent treatment
process depend upon the introduction of improved digester designs at:
· small scale and particularly domestic scale reactor
designs need improving to make them cheaper and capable of delivering maximum
energy yields
· large scale plants need everything needed at the small
scale, plus government support to discourage those that would just throw their
waste in a big hole at a landfill site!
Limitations
concerning thermodynamic efficiency, scrubbing costs, flammability,
compress-ability and storage are also hampering the use of AD plants.
Despite
all this communities and governments are moving ahead with developing anaerobic
digestion technology.
The
overriding concern now developing is the imperative of reducing global warming.
Anaerobic digestion and biogas has a unique role to play in that, and the
quicker that is realized the better.
https://youtu.be/La6yXYwVq3A
The potential for anaerobic
digestion, and the benefits of the biogas process are massive. Discover
mankind's sustainable renewable energy future here! This website is an
independent venture, by people who are simply fascinated by the
subject (read About Us). We
want to help more people see our vision for a vibrant low-carbon future,
and become part of the AD technology movement. You are very welcome
to spend time on this website, and we hope that you will get involved by
commenting, and maybe even joining our campaign for better AD awareness, as
well.



 |
| Anaerobic digestion schematic |



No comments:
Post a Comment